
Causation Definition
Dive Deep: Understanding Causation in Modern Research SHARE THE ARTICLE ON Table of Contents What is Causation? Causation is an important and widely used term

Find the best survey software for you!
(Along with a checklist to compare platforms)
Take a peek at our powerful survey features to design surveys that scale discoveries.
Explore Voxco
Need to map Voxco’s features & offerings? We can help!
Find the best customer experience platform
Uncover customer pain points, analyze feedback and run successful CX programs with the best CX platform for your team.

We’ve been avid users of the Voxco platform now for over 20 years. It gives us the flexibility to routinely enhance our survey toolkit and provides our clients with a more robust dataset and story to tell their clients.
Steve Male
VP Innovation & Strategic Partnerships, The Logit Group
Explore Regional Offices

Find the best survey software for you!
(Along with a checklist to compare platforms)
Take a peek at our powerful survey features to design surveys that scale discoveries.
Explore Voxco
Need to map Voxco’s features & offerings? We can help!
Find the best customer experience platform
Uncover customer pain points, analyze feedback and run successful CX programs with the best CX platform for your team.

We’ve been avid users of the Voxco platform now for over 20 years. It gives us the flexibility to routinely enhance our survey toolkit and provides our clients with a more robust dataset and story to tell their clients.
Steve Male
VP Innovation & Strategic Partnerships, The Logit Group
Explore Regional Offices

Find the best survey software for you!
(Along with a checklist to compare platforms)
Take a peek at our powerful survey features to design surveys that scale discoveries.
Explore Voxco
Need to map Voxco’s features & offerings? We can help!
Find the best customer experience platform
Uncover customer pain points, analyze feedback and run successful CX programs with the best CX platform for your team.

We’ve been avid users of the Voxco platform now for over 20 years. It gives us the flexibility to routinely enhance our survey toolkit and provides our clients with a more robust dataset and story to tell their clients.
Steve Male
VP Innovation & Strategic Partnerships, The Logit Group
Explore Regional Offices
SHARE THE ARTICLE ON
Social research is an approach adopted by sociologists and researchers to learn about people’s day to day lives and design the products that best suit their needs.
People from different parts of the world have different ways of living their social lives. They might have various views about one problem. To satisfy their requirements and know their thoughts and opinions, social research has always proven to be the best solution.
A researcher might want to trigger social research after coming across a new market trend, a new product development or an upgrade to the existing one.
Examples: some examples of social research can be a census of a country, investigation of agricultural lands, literacy rate.
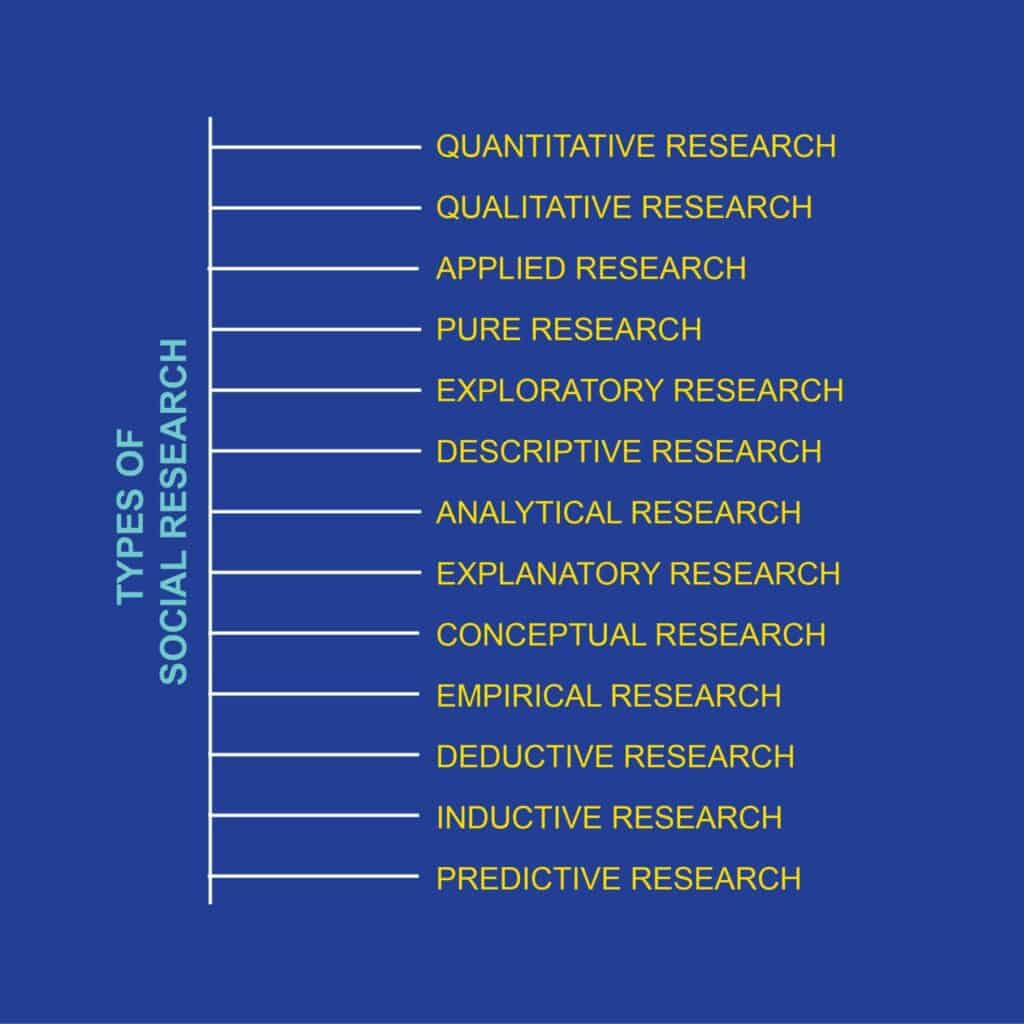
There are various types of research types and you will find different sets of them from different resources. Here are some of the types of social research that are commonly used:
Quantitative research refers to collecting and statistically analyzing numerical data. It helps in finding patterns, predictions, averages in the collected data. Quantitative data is collected through conducting surveys, polls, and interviews.
Example: you want to find out how many people who attended the seminar liked it. You will ask questions like “Did you like the seminar?”
You can use a quantitative research model when you want to have numerical data on which you can perform statistical calculations.
Advantages:
It allows the researcher to reach out to a larger sample size.
Does not require observation.
Research performed is anonymous and can have honest responses.
Disadvantages:
It does not study the reason behind a response.
Quantitative research can be very expensive.
Qualitative research is a type of social research which aims at gathering descriptive opinions of people through open-ended questions in a survey or an interview. The data collected from this research is vast and needs to be summarized to get to a conclusion.
Example: You know what people think about your seminar, but you want to know why they think that way and what changes they want in your next seminar. This will allow responders to briefly tell their views.
This method best suits the research problems that include an in-depth understanding of a topic or a group of people.
Advantages:
It gets to the reason behind the attitude of the responders.
It gives a lot of data to work on.
It is not very costly.
Disadvantages:
It does not statistically represent the data.
There is a chance of data loss due to its large data nature.
The results acquired from this approach can be influenced by the researcher’s personal opinions.
It is research that provides solutions for real-life problems. Researchers use applied research to get to the solutions which they can implement immediately. The problems can be related to health, diet, work-out, etc. the solutions to this research can be technological.
Example: A software solution firm wants to provide a solution that will prompt a message every time someone tries to take a print from the office printer. This will make them consider paper use and can be an initiative towards paper reduction.
Applied research is used in everyday life problems as it can provide solutions in a short period and the solutions are easy to implement as well.
Advantages:
It helps find solutions for a specific business or other settings.
Solutions can be implemented right away.
Disadvantages:
Solutions established from applied research cannot be generalized for other similar problems.
Pure or basic research, unlike applied research, does not concern about providing solutions. This research can be explanatory, exploratory or descriptive. The main objective of this research is to provide a total understanding of a topic.
Example: A researcher conducts a study on how hypertension affects a person’s blood pressure.
Pure or basic research is conducted when you want to understand a problem statement without getting into providing any solution for it. This is the major difference between pure research and applied research.
Advantages:
It expands our knowledge about everyday life.
It covers a large part of the topic.
Disadvantages:
It does not provide the deep learning of how to tackle the problem.

This research is helping to get to solutions for the problems that are not clear. It provides a better understanding of the existing problem but will not provide final solutions. It is conducted at a preliminary stage of the problem and answers questions like why what and how.
Example: A company owner is not sure if he should expand the branch and hence decides to conduct explanatory research. At the end of the research, he will know if it is a good move to expand an extra branch or not.
Exploratory research can be used when you have to study the scope of the existing problem for its future. It can help you find the focus for the future.
Advantages:
The researcher can adapt to the changes during the research.
It costs very low.
It can give solutions for the future of the problems.
Disadvantages:
This research may lead to wrong decisions.
See Voxco survey software in action with a Free demo.
See Voxco survey software in action with a Free demo.
Descriptive research is research that describes the characteristics of the variables. The characteristics can be the answers to the questions like “what, why, how and when”
It is also called observational research as the variables are not changed during the research.
Example: A person wants to set up a café in a particular area, he wants to know what are the preferences of the people from the area regarding similar cafes.
When you want to conduct an observational study without touching the integrity of the variable, descriptive research is the solution for you.
Advantages:
As it uses primary data collection, the data is rich in information.
The survey method can be qualitative and quantitative providing flexibility.
Disadvantages:
Information collected can be misleading.
The researcher’s biases can affect the result.
The size of the sample can have representative issues.
Analytical research focuses on the cause-effect of the variables. While descriptive analysis tells the facts, analytical research determines what the reason behind those facts is.
Example: A descriptive study says almost all elderly people have joint pain. Analytical research can work to find out the reason behind the illness. It can tell how old age affects the bone structure and result in them weakening.
Analytical research come in handy when you have to resolve the “what, when, how and why” of the existing researched topic.
Advantages:
Provides more control over the data.
Determines the reason behind the fact.
It is inexpensive and simple to implement.
Disadvantages:
Can include measurement errors.
Bias in the sample population can affect the results.
This research deals with researchers revisiting phenomenon that were not studied in-depth before. It doesn’t mean that the research has to provide solutions now. It can be done for the sole purpose of understanding the topic.
Example: A researcher wants to study a literature topic. It may include reading through existing researches, magazines, articles.
Explanatory research aims towards finding out why the phenomenon occurred and what are chances of it occurring in the future are.
Advantages:
Allows the researcher to know more about the topic.
Gives a scope to have new solutions.
Disadvantages:
Results can have the researcher’s biases affected.
It includes observing and analyzing the already existing topic. It doesn’t involve any practical research. Researchers state their concepts and ideas regarding the topic. It is just and theoretical ideology of the topic.
Example: Stephan Hawkins had a conceptualization of the black hole on his observation of the universe. Years later we had the first image of a black hole.
Conceptual research is used more in philosophical research. They use it to come up with new concepts and enhance the existing ones.
Advantages:
It requires few resources which saves time and resources.
It uses existing literature hence making it convenient.
Disadvantages:
The results may not be considered reliable and factual.
It is likely to face errors overtime after new concepts are discovered.
Empirical research involves concluding only from verifiable shreds of evidence. This research can be conducted using a qualitative method or quantitative method. The results have a strong background and can be trusted.
Example: A researcher wants to know if listening to motivational speech cause more productivity. He tests this by exposing one group to listen to the motivational speech while the other group doesn’t.
Empirical research is useful when you want to prove a hypothesis based on strong proof. As people need to have something that can be proven, this research provides exactly just that.
Advantages:
This makes the conducted research more authentic.
Strengthens the internal validity.
Disadvantages:
It can be very time-consuming.
Data collection can be challenging as it is supposed to be from an authorized source.
Deductive research is based on an already existing theory. It creates a hypothesis on the theory and then research is done to test if the hypothesis is true. The theories are tested against observations.
Example: All animals drink water. Dog drinks water. The dog is an animal. It is assumed that “all animals drink water” and “dog is an animal” both are correct.
Deductive research stands strong when you have to formulate a hypothesis on a theory, test that hypothesis and examine the results.
Advantages:
It explains the cause-effect relationship between variables.
The results can be generalized to a certain extent.
Disadvantages:
They may not understand the rules.
It can be misrepresenting.
Unlike deductive research, inductive research works with a focus on developing a theory. It goes from observation to generalizations of the topic. Commonly, researchers prefer to combine both pieces of research in case of a huge study.
Example: Observation- Dogs is an animal
Observing a pattern- Dog drinks water
Developing a theory- All animals drink water
Inductive research can be used when you want to understand a topic that does not have enough existing literature. It helps you to observe the topic and then come to conclusions which you can apply in a broader sense.
Advantages:
It can be used to predict what can happen in the future.
It gives deep knowledge about the research topic.
Disadvantages:
The reasoning can be incorrect.
The research is limited to how much you can make a result generalization.
As the name suggests, this research predicts the outcomes, consequences, costs, and other such factors. These factors are calculated for the existing theories. The predictions are mostly about the things that are not tested or tried yet.
Example: A company owner will study the employees’ performances, the projects completed, client satisfaction, speed of project completion, and various other measures to predict the company’s success and growth in the coming years.
Predictive analysis is an efficient method of research when you want to find the probability of a phenomenon occurring shortly. It can be used in all types of research problems and is a common practice.
Advantages:
It has a competitive advantage.
It also helps reduce risks and the costs behind solving them.
Deal with problems before they occur.
Disadvantages:
Data cannot be relied upon totally because people don’t always give honest answers in surveys.
Data collected can be different concerning quality measures.

Dive Deep: Understanding Causation in Modern Research SHARE THE ARTICLE ON Table of Contents What is Causation? Causation is an important and widely used term

Secondary Research: Definition, Methods & Examples The ultimate secondary research guide Upgrade your secondary research with agile market research guide. Download Now SHARE THE ARTICLE
Conducting research studies can be intense! Surveys, analytics, data verification, and monitoring. One of the most rewarding parts of research is when you get to showcase your survey results to your stakeholders.

Survey Fatigue: How to Avoid It? SHARE THE ARTICLE ON Table of Contents Survey fatigue – a universal issue that researchers face all over the

All you need to know about Customer Experience Measurement Tools Customer Experience Ensuring an excellent customer experience can be tricky but an effective guide can

Sentiment Analysis SHARE THE ARTICLE ON Table of Contents Sentiment analysis is a subset of text research, sometimes known as mining. It employs a combination
We use cookies in our website to give you the best browsing experience and to tailor advertising. By continuing to use our website, you give us consent to the use of cookies. Read More
| Name | Domain | Purpose | Expiry | Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| hubspotutk | www.voxco.com | HubSpot functional cookie. | 1 year | HTTP |
| lhc_dir_locale | amplifyreach.com | --- | 52 years | --- |
| lhc_dirclass | amplifyreach.com | --- | 52 years | --- |
| Name | Domain | Purpose | Expiry | Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| _fbp | www.voxco.com | Facebook Pixel advertising first-party cookie | 3 months | HTTP |
| __hstc | www.voxco.com | Hubspot marketing platform cookie. | 1 year | HTTP |
| __hssrc | www.voxco.com | Hubspot marketing platform cookie. | 52 years | HTTP |
| __hssc | www.voxco.com | Hubspot marketing platform cookie. | Session | HTTP |
| Name | Domain | Purpose | Expiry | Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| _gid | www.voxco.com | Google Universal Analytics short-time unique user tracking identifier. | 1 days | HTTP |
| MUID | bing.com | Microsoft User Identifier tracking cookie used by Bing Ads. | 1 year | HTTP |
| MR | bat.bing.com | Microsoft User Identifier tracking cookie used by Bing Ads. | 7 days | HTTP |
| IDE | doubleclick.net | Google advertising cookie used for user tracking and ad targeting purposes. | 2 years | HTTP |
| _vwo_uuid_v2 | www.voxco.com | Generic Visual Website Optimizer (VWO) user tracking cookie. | 1 year | HTTP |
| _vis_opt_s | www.voxco.com | Generic Visual Website Optimizer (VWO) user tracking cookie that detects if the user is new or returning to a particular campaign. | 3 months | HTTP |
| _vis_opt_test_cookie | www.voxco.com | A session (temporary) cookie used by Generic Visual Website Optimizer (VWO) to detect if the cookies are enabled on the browser of the user or not. | 52 years | HTTP |
| _ga | www.voxco.com | Google Universal Analytics long-time unique user tracking identifier. | 2 years | HTTP |
| _uetsid | www.voxco.com | Microsoft Bing Ads Universal Event Tracking (UET) tracking cookie. | 1 days | HTTP |
| vuid | vimeo.com | Vimeo tracking cookie | 2 years | HTTP |
| Name | Domain | Purpose | Expiry | Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| __cf_bm | hubspot.com | Generic CloudFlare functional cookie. | Session | HTTP |
| Name | Domain | Purpose | Expiry | Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| _gcl_au | www.voxco.com | --- | 3 months | --- |
| _gat_gtag_UA_3262734_1 | www.voxco.com | --- | Session | --- |
| _clck | www.voxco.com | --- | 1 year | --- |
| _ga_HNFQQ528PZ | www.voxco.com | --- | 2 years | --- |
| _clsk | www.voxco.com | --- | 1 days | --- |
| visitor_id18452 | pardot.com | --- | 10 years | --- |
| visitor_id18452-hash | pardot.com | --- | 10 years | --- |
| lpv18452 | pi.pardot.com | --- | Session | --- |
| lhc_per | www.voxco.com | --- | 6 months | --- |
| _uetvid | www.voxco.com | --- | 1 year | --- |