
Best Data Collection Tools To Look For in 2024
Best Data Collection Tools To Look For in 2024 SHARE THE ARTICLE ON Table of Contents Data collection software plays a vital role in modern

Find the best survey software for you!
(Along with a checklist to compare platforms)
Take a peek at our powerful survey features to design surveys that scale discoveries.
Explore Voxco
Need to map Voxco’s features & offerings? We can help!
Find the best customer experience platform
Uncover customer pain points, analyze feedback and run successful CX programs with the best CX platform for your team.

We’ve been avid users of the Voxco platform now for over 20 years. It gives us the flexibility to routinely enhance our survey toolkit and provides our clients with a more robust dataset and story to tell their clients.
Steve Male
VP Innovation & Strategic Partnerships, The Logit Group
Explore Regional Offices

Find the best survey software for you!
(Along with a checklist to compare platforms)
Take a peek at our powerful survey features to design surveys that scale discoveries.
Explore Voxco
Need to map Voxco’s features & offerings? We can help!
Find the best customer experience platform
Uncover customer pain points, analyze feedback and run successful CX programs with the best CX platform for your team.

We’ve been avid users of the Voxco platform now for over 20 years. It gives us the flexibility to routinely enhance our survey toolkit and provides our clients with a more robust dataset and story to tell their clients.
Steve Male
VP Innovation & Strategic Partnerships, The Logit Group
Explore Regional Offices

Find the best survey software for you!
(Along with a checklist to compare platforms)
Take a peek at our powerful survey features to design surveys that scale discoveries.
Explore Voxco
Need to map Voxco’s features & offerings? We can help!
Find the best customer experience platform
Uncover customer pain points, analyze feedback and run successful CX programs with the best CX platform for your team.

We’ve been avid users of the Voxco platform now for over 20 years. It gives us the flexibility to routinely enhance our survey toolkit and provides our clients with a more robust dataset and story to tell their clients.
Steve Male
VP Innovation & Strategic Partnerships, The Logit Group
Explore Regional Offices

SHARE THE ARTICLE ON
As a business, you cannot be happy about losing your customers. You would want to keep your customers from going to your competitors. Customer Retention plays a vital role in the success of the company. With an increase of 5% in customer retention, the company profit increases from 25% to 95%. Most successful companies believe customer retention to be the key to growing the revenue and the company.
A customer retention strategy, when used effectively, can help you build a lasting relationship with the customers. Loyal customers are your advocates and promoters. They spread words about your brand to their peers, influencing their purchase decisions. This automatically helps you gain potential customers resulting in an increase in revenue.
Customer retention rate indicates the percentage of consumers you have managed to retain in a period of time.

CRR = [(E-N)/ S] X 100
For example, if for the month of June, on 1st June, you had 1500 customers. By the end of the month, i.e., on 30th June, you have acquired 500 customers but also lost 300 customers.
The total no. of customers at the end of the period, i.e., in the month of June you have 1700 customers left.
CRR = (1700 – 500)/ 1500 X 100
CRR = 80%
Other than the Customer Retention Rate metric there are many more metrics that can help you gather insight for successful customer strategy. These metrics can help you track the health of your business.
Related read: How can Contact Centers Improve their Customer Retention Rate?
→ Expanding its Online Grocery PickUp service to other states.
→ Increase in product variety from 3000 to 7000.
Now, we will look into the different customer retention rate metrics you can track to capture insight into your customer retention. The data will help you identify retention issues and gaps in your strategies.
Customer Retention Cost refers to the total amount of money spent to retain current customers. It is a sum of all kinds of resources utilized to ensure that an existing consumer buys from the brand again in the future.
Customer retention cost = S cost of (CST, RAMT, CEAP, CEAS, PST, CM)
To calculate Customer Retention Cost per Customer (CRCC), you can simply divide the CRC by the total no. of customers you have retained.
CRCC = CRC / total no. of customers retained
Let’s say you have spent a total (CRC) of $80,000, and you have retained 4000 customers in a month. Your Customer Retention Rate per Customer will be
CRCC = $80,000/ 4000 = $20
Calculating CRC helps brands optimize their strategy in order to keep the CRCC lower. Low CRCC implies that the process of customer retention was easy. It also indicates that the retention rate is higher for the business, which means more loyal customers and more profit.
CLV measures the profit generated by a company from a single customer. CLV is a metric that should be monitored regularly. The metric helps determine and segment the customers who are worth retaining and those who are not a priority. A low or sinking CLV implies that you are targeting low-value customers. It can also mean that you are losing customers at a faster rate than in the past.
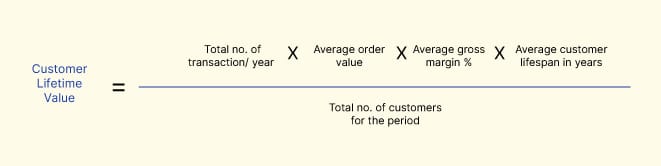
CLV = T X AOV X AGM X ALT / total no. of customers for the period
Say your company manufactures Polaroid cameras, and in the year 2020, you have sold 1 million cameras.
Your AOV is $200, and on every sale, you have a gross margin of 8%. After selling 100,000 cameras, you have attracted 80,000 customers (new and retained). The average lifespan of your Polaroid camera is 1.5 years. This means that your customer will repeat purchases in the same product category after 1.5 years.
So, your CLV is
CLV = (100,000 X 200 X 0.08 X 1.5)/ 80,000 = $30
In this scenario, your CLV is $30.
Revenue Churn Rate indicates the percentage of revenue your company has lost from your existing customers under a certain time period. Calculating your revenue churn rate can help you determine which products or services are not performing well in the market.

Revenue is mostly calculated every quarter instead of every month because monthly revenue data may not show much difference.
For example, for a previous quarter, the revenue was $90,000, and for this quarter, it is $85,000.
So, Revenue churn rate = (90,000 – 85,000)/ 90,000 X 100 = 5.5%
The revenue churn rate is different from the customer churn rate, as we will learn next. The formula may seem similar, but the insights you gather are different.
Customer Churn Rate indicates the percentage of customers you have lost in a specific time period. You can calculate your customer churn rate for a month, a quarter, or a year. Generally, the metric is used to measure the loss of customers in a month.
Customer churn rate = [1 – (no. of customers at the end of the period – no. of new customer/ no. of users at the beginning of the period)] X 100
>> Check out our Customer Churn Rate Calculator
For example, you had 10,000 customers at the beginning of this month, and you gained 1200 more customers. But by the end of the month, you lost 700 customers.
Customer churn rate = [1 – (10500 – 1200)/ 10000] X 100 = 7%
If your customer churn rate is 7%, this means your customer retention rate is 93%. So, by calculating your customer churn rate, you can also understand how well you are performing in retaining your existing customers.
Customer growth rate, as the term already implies, is the percentage by which your customer base is growing over weeks, months, quarters, or years.
With CGR, you can learn how your business is performing. It also shows how effective the marketing and sales efforts are in increasing your customer base.

For example, your online retail business had 2000 customers at the beginning of this month, and you gained 500 new customers. Your retention rate is 70%.
CGR = (500 X 0.7)/ 2000) X 100 = 17.5%
Customer growth helps you control the flow of your business. As a small business =, if your customer growth rate is higher, you may find yourself with low resources to provide your new customers. If the growth is slow, the business expenses will also keep growing. CGR thus helps in allocating your business resources.
When a customer purchases more than once from your brand, it is called a Repeat Purchase Rate. The metric helps marketers learn about the purchase behavior and pattern of the customers after the first purchase. You can adjust your target customers after identifying which type of customers make repeated purchases with your brand.
The metric helps sales and marketing teams determine the success of their customer retention strategies. The repeat purchase rate highlights customer loyalty. This metric can also be applied for services that require renewal of subscription.

Let’s say you own a movie website that requires a quarterly subscription. For Q1, you had 6000 customers subscribing to your channel. By Q2 you had 5000 customers repeating their subscription.
Repeat purchase rate = 5000/ 6000 X 100 = 83.3%
As the term suggests, Product Return Rate indicates the percentage of products sent back to your company out of the total no. Units sold. Product return is not good for any company. It can happen if the product does not meet the customer’s expectations or the product delivered is different from the product advertised. Either way, it harms the customer’s relationship with the company.
Product return rate = (total no. of products sent back/ total no. of products sold) X 100
Let’s say your company sells board games. The previous month you sold 5000 units of board games but 1500 units were returned. Product return rate = (1500/ 5000) X 100 = 30%
Net Promoter Score® is an indicator of a customer’s likelihood to recommend your brand or products/ services to other people. Customers are asked the question of the likelihood of recommendation on a scale of 0 to 10. Based on the rating given by the customers, they are categorized into Promoters (9 or 10), Passives (7 or 8), and Detractors (0 to 6).
NPS® = % of promoters – % of detractors
If your survey 2000 respondents, of which 800 are Promoters, 800 are Passives, and 400 are Detractors.
NPS® = [(800/2000) – (400/2000)] X 100 = 20
>> Deep Dive into your NPS data with a unified view.
This metric indicates the time it takes for a customer before they come back to shop with your brand. This is also an indicator of customer loyalty. A longer time between purchases can result from two causes:
Your product quality is good, so customers don’t need to buy again from you, or Your product/ service is not standing apart in the market
To calculate the metric, you need to segment your customers into two categories: one-time buyers and repeat buyers.
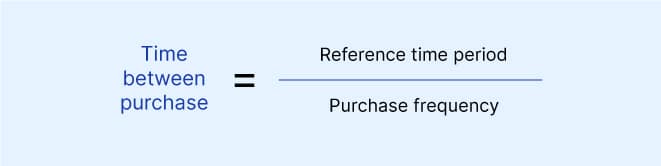
The reference time period is generally considered to be a year, i.e., 365 days. It depends on the industry or the product category that your business is a part of.
If your customers have a purchase frequency of 7 times a year for your product, then your time between purchases is TBP = 365/ 7 = 52.14 days.
Curious About The Price? Click Below To Get A Personalized Quote.
Share of Wallet is an indicator of the total money an average customer spends on your company for a product category rather than on a competing company in the same category. Upselling or cross-selling are two major techniques used by companies to increase a customer’s share of the wallet in order to increase the company’s revenue.
To calculate a customer’s share of wallet for your brand, you need to first list all of your competitors in a specific product category. Then, you need to ask your customer to rank all the brands, including yours, according to their preference (1 being the highest preference).

Let’s say a respondent is given 5 brands to choose from, and they rank your brand as 3rd.
SOW = (1 – 3/6) X 2/5 = 10%
DSO informs the marketer of the average collection period for a company to convert the credit sales into cash. The metrics provide you the no. of days the receivables are outstanding.
Generally, Days Sales Outstanding is calculated on the basis of monthly, quarterly, or annually.
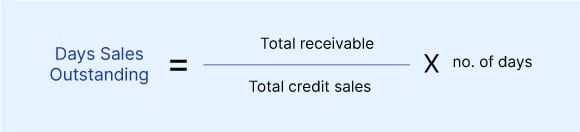
Say, your company, in the past 90 days, has seen a credit sale of $ 150K. You have been able to recover $ 50k in the same time period, which leaves you with total receivables of $100k.
DSO = (100,000/ 150,000) X 90 = 60 days
A loyal customer rate gives you the number of customers who purchased more than once from your brand within a specific time period. The metric is a key indicator of who your loyal customers are. It identifies the customers who contribute the most to your business.
These customers may not drive a lot of sales, but they are loyal advocates of your brand. These customers are satisfied with your brand and do not expect too much from you. By identifying these loyal customers, you can obtain testimonials from them to promote your business.

Let’s say, you had 10k customers in the month of January, of which 6k customers made multiple purchases.
Loyal customer rate = 6000/10,000 = 60%.
Related read: 8 Effective Strategies to Reduce Churn in 2023
See how we can enhance your research efficiency.
Most business model drive their revenue from repeat customers. This means you need to focus on your retention strategy and proactively reduce churn over acquisition. Customer retention brings financial stability to your business, enhances customer loyalty, and boosts brand advocacy.
Tracking customer retention metrics is more than a performance indicator, it is a strategy necessary for long-term business success. Measuring the metrics empowers you to build lasting relationships, maximize revenue, and stay ahead of competitions.
You can use any of these customer retention metrics or a combination of them to gain more insight into how your customer retention program is performing. Collecting and quantifying these metric values is not the end of the task. You must record them and share them with different departments to gather everyone’s opinion on how to improve customer retention.
Read more

Best Data Collection Tools To Look For in 2024 SHARE THE ARTICLE ON Table of Contents Data collection software plays a vital role in modern

Mastering Survey Data Visualization SHARE THE ARTICLE ON Table of Contents Conducting surveys and gathering data is easy. However, the right insights often get buried

Survey Software User Guide: What You Need to Know SHARE THE ARTICLE ON Table of Contents In the research landscape teeming with options, choosing the
Customer Engagement Metrics For Business Success SHARE THE ARTICLE ON Table of Contents In the fast-paced world of business, understanding how to effectively engage with

Top 10 feedback collection tools in 2024 SHARE THE ARTICLE ON Table of Contents Collecting feedback is necessary for businesses and organizations to understand their

Top 5 Customer Engagement Metrics to Measure in 2024 SHARE THE ARTICLE ON Table of Contents As we navigate through 2024, we must be aware
We use cookies in our website to give you the best browsing experience and to tailor advertising. By continuing to use our website, you give us consent to the use of cookies. Read More
| Name | Domain | Purpose | Expiry | Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| hubspotutk | www.voxco.com | HubSpot functional cookie. | 1 year | HTTP |
| lhc_dir_locale | amplifyreach.com | --- | 52 years | --- |
| lhc_dirclass | amplifyreach.com | --- | 52 years | --- |
| Name | Domain | Purpose | Expiry | Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| _fbp | www.voxco.com | Facebook Pixel advertising first-party cookie | 3 months | HTTP |
| __hstc | www.voxco.com | Hubspot marketing platform cookie. | 1 year | HTTP |
| __hssrc | www.voxco.com | Hubspot marketing platform cookie. | 52 years | HTTP |
| __hssc | www.voxco.com | Hubspot marketing platform cookie. | Session | HTTP |
| Name | Domain | Purpose | Expiry | Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| _gid | www.voxco.com | Google Universal Analytics short-time unique user tracking identifier. | 1 days | HTTP |
| MUID | bing.com | Microsoft User Identifier tracking cookie used by Bing Ads. | 1 year | HTTP |
| MR | bat.bing.com | Microsoft User Identifier tracking cookie used by Bing Ads. | 7 days | HTTP |
| IDE | doubleclick.net | Google advertising cookie used for user tracking and ad targeting purposes. | 2 years | HTTP |
| _vwo_uuid_v2 | www.voxco.com | Generic Visual Website Optimizer (VWO) user tracking cookie. | 1 year | HTTP |
| _vis_opt_s | www.voxco.com | Generic Visual Website Optimizer (VWO) user tracking cookie that detects if the user is new or returning to a particular campaign. | 3 months | HTTP |
| _vis_opt_test_cookie | www.voxco.com | A session (temporary) cookie used by Generic Visual Website Optimizer (VWO) to detect if the cookies are enabled on the browser of the user or not. | 52 years | HTTP |
| _ga | www.voxco.com | Google Universal Analytics long-time unique user tracking identifier. | 2 years | HTTP |
| _uetsid | www.voxco.com | Microsoft Bing Ads Universal Event Tracking (UET) tracking cookie. | 1 days | HTTP |
| vuid | vimeo.com | Vimeo tracking cookie | 2 years | HTTP |
| Name | Domain | Purpose | Expiry | Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| __cf_bm | hubspot.com | Generic CloudFlare functional cookie. | Session | HTTP |
| Name | Domain | Purpose | Expiry | Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| _gcl_au | www.voxco.com | --- | 3 months | --- |
| _gat_gtag_UA_3262734_1 | www.voxco.com | --- | Session | --- |
| _clck | www.voxco.com | --- | 1 year | --- |
| _ga_HNFQQ528PZ | www.voxco.com | --- | 2 years | --- |
| _clsk | www.voxco.com | --- | 1 days | --- |
| visitor_id18452 | pardot.com | --- | 10 years | --- |
| visitor_id18452-hash | pardot.com | --- | 10 years | --- |
| lpv18452 | pi.pardot.com | --- | Session | --- |
| lhc_per | www.voxco.com | --- | 6 months | --- |
| _uetvid | www.voxco.com | --- | 1 year | --- |