How to Create a Customer Experience that Fits your Brand
How to Create a Customer Experience that Fits your Brand SHARE THE ARTICLE ON Table of Contents Introduction In order to investigate what customers believe

Find the best survey software for you!
(Along with a checklist to compare platforms)
Take a peek at our powerful survey features to design surveys that scale discoveries.
Explore Voxco
Need to map Voxco’s features & offerings? We can help!
Find the best customer experience platform
Uncover customer pain points, analyze feedback and run successful CX programs with the best CX platform for your team.

We’ve been avid users of the Voxco platform now for over 20 years. It gives us the flexibility to routinely enhance our survey toolkit and provides our clients with a more robust dataset and story to tell their clients.
Steve Male
VP Innovation & Strategic Partnerships, The Logit Group
Explore Regional Offices

Find the best survey software for you!
(Along with a checklist to compare platforms)
Take a peek at our powerful survey features to design surveys that scale discoveries.
Explore Voxco
Need to map Voxco’s features & offerings? We can help!
Find the best customer experience platform
Uncover customer pain points, analyze feedback and run successful CX programs with the best CX platform for your team.

We’ve been avid users of the Voxco platform now for over 20 years. It gives us the flexibility to routinely enhance our survey toolkit and provides our clients with a more robust dataset and story to tell their clients.
Steve Male
VP Innovation & Strategic Partnerships, The Logit Group
Explore Regional Offices

Find the best survey software for you!
(Along with a checklist to compare platforms)
Take a peek at our powerful survey features to design surveys that scale discoveries.
Explore Voxco
Need to map Voxco’s features & offerings? We can help!
Find the best customer experience platform
Uncover customer pain points, analyze feedback and run successful CX programs with the best CX platform for your team.

We’ve been avid users of the Voxco platform now for over 20 years. It gives us the flexibility to routinely enhance our survey toolkit and provides our clients with a more robust dataset and story to tell their clients.
Steve Male
VP Innovation & Strategic Partnerships, The Logit Group
Explore Regional Offices
SHARE THE ARTICLE ON

In the ever-evolving landscape of market research, survey software has emerged as a game-changer. Revolutionizing the traditional methods of data collection, these digital tools have ushered in a new era of efficiency and precision. This introduction explores the profound impact of survey software on market research, highlighting its role in streamlining processes, ensuring data accuracy, and broadening the scope of insights by transcending geographical boundaries. As we delve deeper, we will uncover the key ways in which survey software is reshaping the field of market research and driving informed decision-making in businesses worldwide.
Data collection in the context of market research refers to the process of gathering, recording, and assembling information and data related to a specific market or target audience. It is a crucial step in market research that involves collecting various types of data to gain insights into consumer behavior, preferences, trends, and other relevant information that can be used to make informed business decisions.
Data collection is crucial for several reasons, particularly in the context of market research and business decision-making:
Data provides the basis for making informed and evidence-based decisions. Without data, decisions may be based on intuition or assumptions, which can lead to costly mistakes.
Data collection helps businesses gain a deeper understanding of their target audience, including their needs, preferences, and behaviors. This knowledge can be used to tailor products, services, and marketing efforts to better meet customer expectations.
Data collection in market research allows businesses to analyze market trends, identify opportunities, and assess the competitive landscape. This information is essential for strategic planning and market positioning.
By collecting data, businesses can identify potential risks and challenges in their operations or market conditions. This enables proactive risk management and the development of contingency plans.
Data helps in the development of new products or the improvement of existing ones. Customer feedback and market research data can inform product features, pricing, and quality enhancements.
Data collection helps measure the effectiveness of marketing campaigns and strategies. It allows businesses to allocate resources efficiently and refine marketing efforts based on real-time feedback.
Data collection is the process of gathering and measuring information on variables of interest in a systematic and organized manner. There are various types of data collection methods, each suitable for different research objectives and contexts. Here are 5 common types of data collection:
Surveys involve asking questions to a sample of individuals or organizations to collect data on their opinions, attitudes, behaviors, or characteristics. Surveys can be conducted through various means, including online surveys, paper questionnaires, telephone interviews, or face-to-face interviews.
This method involves systematically watching and recording behaviors, events, or phenomena in their natural settings. Observational data can be collected through direct observations (researchers are physically present) or indirect observations (using cameras, sensors, or other technology).
Experiments are conducted to test hypotheses and establish cause-and-effect relationships. Researchers manipulate one or more independent variables and observe the effects on dependent variables. Experimental data collection in market research often occurs in controlled environments.
Interviews involve direct communication between a researcher and a respondent. They can be structured (with a fixed set of questions), semi-structured (with some flexibility in question order or wording), or unstructured (open-ended discussions). Interviews can be conducted in person, over the phone, or via video conferencing.
Focus groups are group discussions led by a moderator to gather qualitative data on participants’ opinions, perceptions, and experiences. They are useful for exploring complex issues and understanding group dynamics
Collecting data in market research is a critical step in understanding consumer preferences, behaviors, and market trends. It involves gathering information to make informed business decisions. Here’s how data collection typically works:
Start by clearly defining the objectives of your market research. What specific information are you trying to gather, and what decisions will be based on this data? Understanding your research goals is crucial for designing an effective data collection strategy.
Select the most appropriate data collection methods for your research. Common methods include surveys, interviews, focus groups, observations, and secondary data analysis. The choice of method will depend on your research goals, budget, and timeline.
If you opt for surveys or interviews, you’ll need to create questionnaires or interview guides. These instruments should contain clear, unbiased, and relevant questions to collect the data you need. Consider pre-testing your instruments with a small group to identify any issues.
Determine the population or group you want to study and select a sample that represents this population. The sample size and selection method will depend on your research goals and the statistical accuracy you require.
Conduct data collection in market research by administering surveys, conducting interviews, or facilitating focus group discussions. Ensure that data collection is carried out consistently and follows the research plan.
After data collection, if you have paper-based surveys or other physical data, it needs to be entered into a digital format for analysis. Data entry should be accurate to minimize errors.
Review and clean the collected data to identify and correct errors, inconsistencies, or missing information. This ensures the quality and reliability of the dataset.
Analyze the collected data using statistical tools, software, or qualitative analysis methods, depending on the nature of your research. The goal is to extract meaningful insights and identify patterns and trends.
Summarize and interpret the research findings in a clear and actionable report. Include visual aids like charts and graphs to make the data more accessible to stakeholders.
Use the research findings to make informed business decisions, such as product development, marketing strategies, pricing, and market segmentation.
Market research is often an ongoing process. Companies may conduct regular surveys or data collection to track changes in consumer preferences and market dynamics over time.
Data collection is a crucial step in research and decision-making processes, but it comes with several common challenges that researchers and organizations may face:
Collecting data effectively using survey software involves careful planning, design, distribution, and analysis of your surveys. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you gather high-quality data using survey software:
Clearly outline the purpose of your survey and what you hope to achieve.
Determine the target audience for your survey, as this will influence your survey’s design and distribution.
Research and select survey software that aligns with your needs and budget. Some popular options include SurveyMonkey, Google Forms, Typeform, and Qualtrics.
Create clear and concise questions. Use simple language and avoid jargon.
Use a mix of question types, such as multiple-choice, Likert scale, open-ended, and demographic questions.
Arrange questions logically, starting with easy-to-answer questions to engage respondents and build momentum.
Test your survey with a small group of people to identify and fix any issues.
Make sure your survey is accessible to individuals with disabilities, adhering to accessibility standards such as WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines).
Assure respondents that their responses will remain confidential and that their personal information will not be shared or sold.
Implement data protection measures to comply with relevant privacy regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA).
Before launching your survey, conduct a pilot test with a small group to identify any problems with question clarity or survey flow.
Decide how you will distribute your survey. Options include email invitations, social media, website embedding, or sharing a link.
Consider using incentives (e.g., gift cards, discounts) to encourage participation.
Monitor survey responses as they come in to ensure data quality and detect any issues.
Set a deadline for responses to create a sense of urgency among respondents.
Export survey data into a format suitable for analysis (e.g., CSV, Excel).
Use data analysis tools or software to clean, organize, and analyze the data.
Generate descriptive statistics, create visualizations, and perform more advanced statistical analyses if necessary.
Draw conclusions based on the data and relate them to your research objectives.
Consider the implications of your findings and how they can inform your decision-making.
Create a clear and concise report summarizing the survey results.
Share your findings with stakeholders, colleagues, or the public, as appropriate.
Use the survey data to make informed decisions, drive improvements, or implement changes based on the feedback received.
Consider conducting follow-up surveys or interviews to gain deeper insights or track changes over time.
Survey software has brought a transformative shift to market research by enhancing efficiency, reach, and data accuracy. Its cost-effectiveness, real-time analytics, and customization options have made it an indispensable tool. With a global reach and a commitment to data security, survey software is enabling businesses to gain deeper insights and make informed decisions, ultimately revolutionizing the way market research is conducted in today’s digital age.
How to Create a Customer Experience that Fits your Brand SHARE THE ARTICLE ON Table of Contents Introduction In order to investigate what customers believe
E-commerce Customer Journey Map SHARE THE ARTICLE ON Table of Contents Customers nowadays spend a significant amount of time exploring and comparing all of their

Cogeco Voxco Online SHARE THE ARTICLE ON Online surveys of listener panels help radio stations reach top of the charts. The Client Cogeco is

How to do a customer loss survey? SHARE THE ARTICLE ON Table of Contents Customer loss surveys play a vital role in understanding why customers
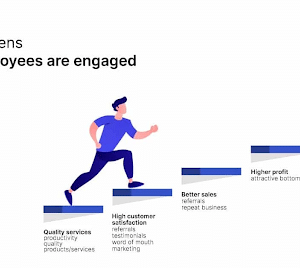
10 Best Employee Satisfaction Survey Questions and Why You Must Ask Them SHARE THE ARTICLE ON Table of Contents Employees who are pleased with their

Unlock The Power Of Branded Surveys SHARE THE ARTICLE ON Table of Contents The survey is a part of the customer experience. When you are
We use cookies in our website to give you the best browsing experience and to tailor advertising. By continuing to use our website, you give us consent to the use of cookies. Read More
| Name | Domain | Purpose | Expiry | Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| hubspotutk | www.voxco.com | HubSpot functional cookie. | 1 year | HTTP |
| lhc_dir_locale | amplifyreach.com | --- | 52 years | --- |
| lhc_dirclass | amplifyreach.com | --- | 52 years | --- |
| Name | Domain | Purpose | Expiry | Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| _fbp | www.voxco.com | Facebook Pixel advertising first-party cookie | 3 months | HTTP |
| __hstc | www.voxco.com | Hubspot marketing platform cookie. | 1 year | HTTP |
| __hssrc | www.voxco.com | Hubspot marketing platform cookie. | 52 years | HTTP |
| __hssc | www.voxco.com | Hubspot marketing platform cookie. | Session | HTTP |
| Name | Domain | Purpose | Expiry | Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| _gid | www.voxco.com | Google Universal Analytics short-time unique user tracking identifier. | 1 days | HTTP |
| MUID | bing.com | Microsoft User Identifier tracking cookie used by Bing Ads. | 1 year | HTTP |
| MR | bat.bing.com | Microsoft User Identifier tracking cookie used by Bing Ads. | 7 days | HTTP |
| IDE | doubleclick.net | Google advertising cookie used for user tracking and ad targeting purposes. | 2 years | HTTP |
| _vwo_uuid_v2 | www.voxco.com | Generic Visual Website Optimizer (VWO) user tracking cookie. | 1 year | HTTP |
| _vis_opt_s | www.voxco.com | Generic Visual Website Optimizer (VWO) user tracking cookie that detects if the user is new or returning to a particular campaign. | 3 months | HTTP |
| _vis_opt_test_cookie | www.voxco.com | A session (temporary) cookie used by Generic Visual Website Optimizer (VWO) to detect if the cookies are enabled on the browser of the user or not. | 52 years | HTTP |
| _ga | www.voxco.com | Google Universal Analytics long-time unique user tracking identifier. | 2 years | HTTP |
| _uetsid | www.voxco.com | Microsoft Bing Ads Universal Event Tracking (UET) tracking cookie. | 1 days | HTTP |
| vuid | vimeo.com | Vimeo tracking cookie | 2 years | HTTP |
| Name | Domain | Purpose | Expiry | Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| __cf_bm | hubspot.com | Generic CloudFlare functional cookie. | Session | HTTP |
| Name | Domain | Purpose | Expiry | Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| _gcl_au | www.voxco.com | --- | 3 months | --- |
| _gat_gtag_UA_3262734_1 | www.voxco.com | --- | Session | --- |
| _clck | www.voxco.com | --- | 1 year | --- |
| _ga_HNFQQ528PZ | www.voxco.com | --- | 2 years | --- |
| _clsk | www.voxco.com | --- | 1 days | --- |
| visitor_id18452 | pardot.com | --- | 10 years | --- |
| visitor_id18452-hash | pardot.com | --- | 10 years | --- |
| lpv18452 | pi.pardot.com | --- | Session | --- |
| lhc_per | www.voxco.com | --- | 6 months | --- |
| _uetvid | www.voxco.com | --- | 1 year | --- |